The global conversation surrounding energy production has increasingly shifted towards sustainability and environmental preservation in recent years. This transition is driven by the urgent need to combat climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and secure a stable and clean energy supply for future generations. Renewable energy technologies have emerged as a beacon of hope in this context, offering numerous benefits over traditional fossil fuel-based systems. In this article, we will explore the various types and benefits of renewable energy technologies, the economy, and the environment.
Types of Renewable Energy Technologies
Renewable energy technologies harness natural processes to generate electricity and other forms of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and emit harmful pollutants, renewable resources are abundant and produce little to no emissions. The primary types of renewable energy technologies include:
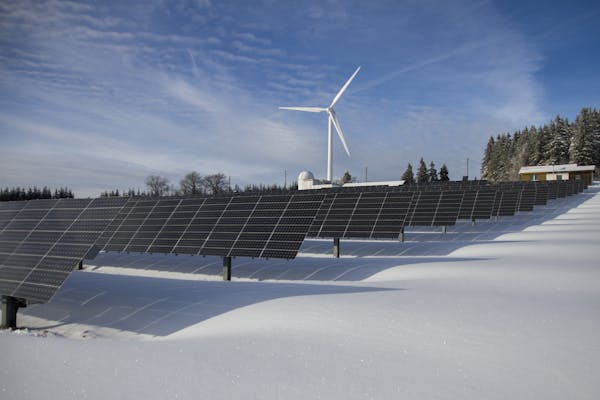
- Solar Energy: Solar power harnesses the energy from the sun using photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar thermal systems. PV cells convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal systems concentrate sunlight to heat a fluid, which then generates steam to drive turbines.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of wind and convert it into electricity. Wind farms, both onshore and offshore, are increasingly being deployed to harness this energy source.
- Hydropower: This technology generates electricity by using the flow of water, typically from rivers or dams, to turn turbines. Hydropower is one of the oldest and most established forms of renewable energy.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as plant and animal waste. It can be converted into electricity, heat, or biofuels through processes like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal power plants utilize the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity. This heat can be accessed by drilling wells into geothermal reservoirs.
- Ocean Energy: Ocean energy technologies, including tidal and wave energy, exploit the kinetic and thermal energy from the ocean to produce electricity.
The Mechanisms Behind Renewable Energy Technologies
Understanding how these technologies work is crucial to appreciating their benefits. Each type of renewable energy technology has a unique mechanism for capturing and converting natural energy sources:
- Solar PV Cells: Composed of semiconductor materials, PV cells absorb photons from sunlight, causing electrons to become excited and create an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect.
- Wind Turbines: As wind moves the blades of a turbine, it spins a shaft connected to a generator, which produces electricity. The efficiency of wind turbines depends on factors such as blade design, wind speed, and turbine height.
- Hydropower: In a hydropower system, water flow turns a turbine connected to a generator. The potential energy of the water is converted into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy.
- Biomass Conversion: Biomass can be burned directly to produce heat, or it can be processed into biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel. In advanced systems, biomass can be gasified to produce syngas, which can then be used to generate electricity or produce chemicals.
- Geothermal Plants: Geothermal power plants use steam produced from hot water reservoirs deep beneath the Earth’s surface. The steam drives turbines connected to generators, producing electricity.
- Ocean Energy Systems: Tidal energy exploits the rise and fall of sea levels, while wave energy harnesses the movement of the ocean’s surface. Both systems use mechanical devices to capture energy, which is then converted into electricity.
The Benefits of Renewable Energy Technologies
The shift towards renewable energy technologies is driven by a multitude of benefits. These benefits encompass environmental, economic, and social aspects, making renewable energy an attractive option for a sustainable future.
1. Environmental Benefits
The most significant environmental benefit of renewable energy technologies is their ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants when burned, renewable energy sources produce little to no emissions. This reduction in emissions is crucial in the fight against climate change, as it helps to stabilize atmospheric CO2 levels and mitigate global warming.
Additionally, renewable energy technologies often have a lower environmental impact compared to conventional energy sources. For instance, solar panels and wind turbines require less water for operation than coal or nuclear power plants, reducing the strain on local water resources. Moreover, renewable energy projects typically have a smaller land footprint and cause less habitat disruption compared to mining and drilling for fossil fuels.
2. Economic Benefits
The transition to renewable energy technologies also brings significant economic advantages. One of the most notable benefits is job creation. The renewable energy sector is labor-intensive, requiring a skilled workforce for the design, installation, and maintenance of energy systems. As countries invest in renewable energy infrastructure, new job opportunities are created in engineering, manufacturing, construction, and research and development.
Furthermore, renewable energy technologies can enhance energy security and reduce dependence on imported fuels. By harnessing local renewable resources, countries can produce their own energy, reducing vulnerability to global energy market fluctuations and geopolitical tensions. This energy independence can lead to more stable energy prices and a more resilient economy.
3. Social Benefits
Renewable energy technologies offer several social benefits, particularly in terms of public health and quality of life. The reduction in air and water pollution from renewable energy sources leads to improved air quality and a decrease in respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Cleaner air and water also contribute to better overall public health and a higher quality of life for communities.
Additionally, renewable energy projects can empower local communities by providing access to affordable and reliable energy. In many remote and underserved areas, renewable energy systems like solar panels and wind turbines offer a viable solution for electrification, reducing energy poverty and supporting economic development.
4. Technological Innovation and Sustainability
The adoption of renewable energy technologies drives technological innovation and fosters a culture of sustainability. As the demand for renewable energy grows, so does the need for advanced materials, efficient storage solutions, and smart grid technologies. This innovation not only improves the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy systems but also has spillover effects in other industries, promoting a more sustainable economy.
Moreover, the transition to renewable energy is closely linked to the concept of sustainability. By utilizing resources that are naturally replenished, renewable energy technologies promote a sustainable energy model that can meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This sustainable approach is essential for long-term economic growth and environmental stewardship.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of renewable energy technologies are substantial, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and considerations associated with their deployment.
1. Intermittency and Energy Storage
One of the primary challenges of renewable energy technologies, particularly solar and wind power, is intermittency. The availability of sunlight and wind varies with time and weather conditions, making it challenging to ensure a consistent energy supply. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, are crucial to address this issue. These technologies can store excess energy generated during peak production periods and release it when demand is high or when renewable sources are not available.
2. Initial Costs and Investment
The initial costs of renewable energy systems can be high, especially for large-scale projects like offshore wind farms and concentrated solar power plants. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced fuel costs and lower operational expenses, often outweigh these initial investments. Additionally, technological advancements and economies of scale are driving down the costs of renewable energy technologies, making them increasingly competitive with conventional energy sources.
3. Grid Integration and Infrastructure
Integrating renewable energy into existing power grids requires careful planning and infrastructure upgrades. The variability of renewable energy sources can pose challenges to grid stability and reliability. To address these challenges, grid operators must implement advanced forecasting, demand response, and grid management technologies. Upgrading transmission and distribution infrastructure is also essential to accommodate the decentralized nature of renewable energy generation.
4. Land Use and Environmental Impact
While renewable energy technologies generally have a lower environmental impact than fossil fuels, they are not entirely without consequences. For example, large solar farms and wind farms require significant land areas, which can lead to habitat disruption and land-use conflicts. Careful site selection, environmental assessments, and mitigation strategies are necessary to minimize these impacts.
The Future of Renewable Energy Technologies
The future of renewable energy technologies is bright, driven by a global commitment to sustainability, technological advancements, and supportive policies. Governments, businesses, and individuals are increasingly recognizing the importance of transitioning to a clean energy economy.
1. Policy Support and Global Cooperation
Government policies and international agreements play a crucial role in promoting renewable energy adoption. Incentives such as tax credits, feed-in tariffs, and renewable portfolio standards encourage investment in renewable energy projects. Global cooperation, exemplified by agreements like the Paris Agreement, fosters a collective effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
2. Technological Innovations
Technological innovations continue to enhance the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy technologies. Advances in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, and energy storage solutions are driving down costs and improving performance. Breakthroughs in emerging technologies, such as floating offshore wind farms and advanced biofuels, hold promise for expanding the range of renewable energy options.
3. Decentralized Energy Systems
The rise of decentralized energy systems, also known as distributed generation, is transforming the energy landscape. Rooftop solar panels, small wind turbines, and microgrids empower individuals and communities to generate their own electricity. This decentralization enhances energy resilience, reduces transmission losses, and enables greater participation in the energy market.
4. The Role of Consumers
Consumers play a vital role in the transition to renewable energy technologies. As awareness of the benefits of renewable energy technologies grows, more individuals are choosing to install solar panels, invest in electric vehicles, and support green energy initiatives. This consumer-driven demand is accelerating the adoption of renewable energy and encouraging businesses to prioritize sustainability.
Conclusion
Renewable energy technologies represent a transformative force in the global energy landscape. By harnessing the power of natural resources, these technologies offer a multitude of benefits, including environmental protection, economic growth, public health improvements, and technological innovation. While challenges remain, the continued advancement and adoption of renewable energy technologies are essential for building a sustainable and resilient future. As we move forward, embracing the benefits of renewable energy technologies will be crucial in addressing the pressing challenges of climate change and ensuring a prosperous and sustainable world for future generations.